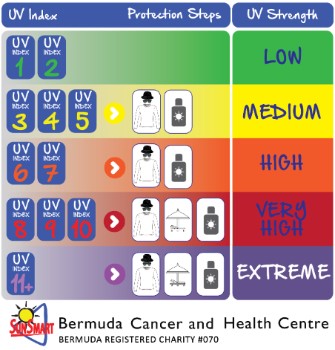
UV Index
The UV Index represents the amount of skin damaging UV radiation reaching the earth’s surface at any instance of time.
The UV Index is a useful tool to help people take steps to reduce their exposure to solar UV radiation. It is reported as a prediction of the UV level at noon, although the actual UV level rises and falls as the day progresses.
- The UV Index level may vary on any given day
- Too much exposure to UV radiation and the number of sunburns experienced, especially during childhood, increases your risk of skin cancer.
- Exposure to UV radiation enables the body to produce vitamin D, an important nutrient in bone development and maintenance. A balance is required between UV radiation exposure for vitamin D production and protecting the skin from damage and skin cancer.
- Most people achieve adequate vitamin D levels through UVB exposure during typical day-to-day outdoor activities. In summer you just need to expose your face, arms and hands or the equivalent area of skin for a few minutes of sunlight each day on either side of the peak UV periods. Naturally dark skinned individuals need longer exposure.
There are three types of UV radiation: UVA, UVB and UVC.
- UVA is principally responsible for aging of the skin.
- UVB and UVA are key contributors for skin cancer.
- UVB is responsible for burning.
- UVC is blocked by the ozone layer
The Bermuda Weather Service now posts a daily UV risk.
Check the UV Index when:
- Planning or participating in an outdoor activity or event
- Involved in recreational activities such as running, swimming, cycling or team sports
- Watching a spectator sport, such as tennis or cricket
- Working outdoors, or have responsibility for out-door workers, or
- Responsible for children or adolescents and their outdoor activities.
When SunSmart UV Alert times apply, you need to be SunSmart during the period indicated.